To quickly identify and resolve indexing issues, start by entering your URL into the Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool. It provides real-time insights into how Google views your page, highlights any crawling problems, and offers suggestions for fixing them. Using this tool can dramatically speed up troubleshooting and improve your site’s visibility in search results.
The URL inspection tool is your go-to resource for pinpointing indexing problems efficiently. By examining individual URLs, you can see whether they are properly indexed, detect any errors, and request reindexing after fixing issues. This makes it easier to keep your website optimized and ensure your pages appear prominently in search engines.
If you’re struggling with why some of your pages aren’t appearing in Google search, the URL inspection tool can be a game-changer. It allows you to analyze specific pages, identify potential issues causing non-indexing, and take immediate action to fix those problems. This straightforward process helps you maintain a healthy website and boosts your SEO performance. In this guide, we’ll walk through how to use this powerful tool effectively, ensuring your website gets the visibility it deserves.
How to Use URL Inspection Tool for Indexing Issues
Understanding the Importance of the URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console helps you see how Google views your web pages. It shows whether a page is indexed, crawling errors, and other technical details. Using this tool is essential to identify and fix problems that prevent your pages from appearing in search results.
Accessing the URL Inspection Tool
To get started, log into your Google Search Console account. On the dashboard, locate the left sidebar and click on “URL Inspection.” Enter the exact URL you want to check in the search bar at the top. Press Enter, and the tool will retrieve data about that specific URL.
Analyzing the Page’s Indexing Status
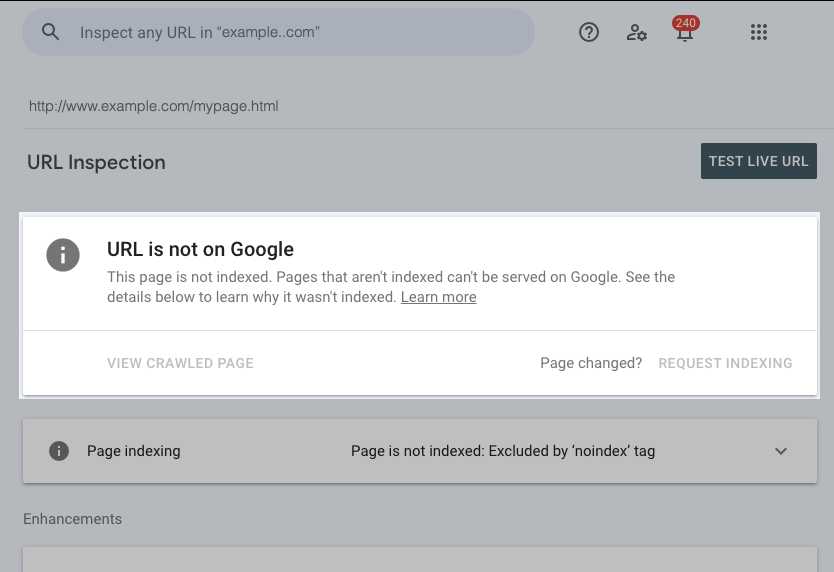
Once the URL loads, you will see the current index status. It might say “Indexed,” “Not Indexed,” or indicate that Google has encountered problems. If your page is indexed, you can verify its appearance in search results. If not, review the reasons provided to understand what prevents indexing.
What Does the Indexing Status Mean?
- Indexed: The page appears in Google search results.
- Not Indexed: Google has not included this page in its index.
- URL blocked or removed: The page is restricted by robots.txt or meta tags.
Checking for Crawl Errors
The tool provides information on crawl issues that might hinder Google from accessing your page. These errors include server errors, 404 not found pages, and redirect problems. Fixing these errors is critical to ensure your page becomes or remains visible in search.
Common Crawl Error Types
- Server Errors (5xx): Indicate server-side problems that prevent crawling.
- 404 Not Found: The URL does not exist at the specified address.
- Redirect Errors: Issues with URL redirects that cause confusion.
Understanding Coverage Information
The Coverage report shows detailed data about the indexing status of your pages. It highlights errors, warnings, and valid pages. Review this data to identify issues that prevent pages from being indexed properly.
Common Coverage Issues
- Excluded pages: These pages may have noindex tags or robots.txt rules blocking them.
- Duplicate content: Google may exclude pages with duplicate content to avoid confusion.
- Submitted URL not selected as canonical: Google prefers a different URL as the primary version.
Requesting Indexing for Your Page
If your URL is not indexed or you have made significant updates, you can request Google to re-crawl the page. Click on “Test Live URL” to see if Google can access the page now. If successful, click “Request Indexing” to expedite the process.
How to Request Indexing Effectively
- Ensure the page is accessible and loads correctly in your browser.
- Remove any indexing barriers like noindex tags or robots.txt restrictions.
- Make significant content updates if necessary before requesting recrawling.
Using the “View Crawled Page” Feature
The tool allows you to see how Googlebot views your page. This view shows the HTML code and how key elements appear to Google. It helps you identify issues like missing meta tags, incorrect canonical links, or problematic JavaScript.
Steps to View the Crawled Page
- In the URL Inspection tool, after retrieving the URL data, click on “View Crawled Page.”
- Review the page layout, especially focusing on important elements like titles, descriptions, and content.
- Check for errors such as blocked resources or missing data.
Inspecting Mobile and Desktop Versions
Google considers mobile-friendliness as a ranking factor. The URL Inspection Tool allows you to see how your page appears on both desktop and mobile devices. Use this feature to identify any mobile usability issues that could affect indexing.
Mobile-Friendly Testing Tips
- Ensure the text is readable without zooming.
- Check that buttons and links are easily clickable.
- Verify that images load correctly on mobile devices.
Understanding and Fixing Meta Tag Issues
Meta tags such as “noindex,” “nofollow,” and canonical tags influence how Google indexes your pages. The inspection tool displays whether these tags are present and correctly set.
Common Meta Tag Problems
- Noindex tags: Block pages from being indexed unintentionally.
- Incorrect canonical tags: Lead to duplicate content issues.
- Missing meta descriptions: Affect how your page appears in search results.
Optimizing URLs to Improve Indexing
Proper URL structures make crawling and indexing easier. Use clear, descriptive URLs with relevant keywords. Avoid overly long or complex URLs that can confuse crawlers.
Best Practices for URL Structure
- Use hyphens to separate words for readability.
- Keep URLs short but descriptive.
- Avoid unnecessary parameters or session IDs.
Monitoring and Maintaining Your Indexing Status
Regular use of the URL Inspection Tool helps you stay on top of your pages’ indexing health. Check important pages periodically and fix issues as they arise to maintain good visibility.
Tips for Ongoing Monitoring
- Set up regular checks for high-traffic pages.
- Track changes in indexing status after content updates.
- Address crawl errors promptly to prevent long-term issues.
Additional Tips for Resolving Indexing Problems
Some issues require technical fixes beyond what the URL Inspection Tool can directly address. Consider consulting a developer for server errors or complex canonical issues.
Other Considerations
- Ensure your sitemap is up-to-date and submitted to Google.
- Use structured data to help Google understand your content better.
- Remove outdated or duplicate pages from your site.
By understanding and properly utilizing the URL Inspection Tool, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve indexing issues. This process helps improve your website’s visibility and ensures your valuable content reaches the right audience through search engines.
Getting the most out of the URL inspection tool
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I interpret the insights provided by the URL Inspection Tool regarding indexing issues?
When you analyze a URL with the inspection tool, pay attention to the status reports and any errors listed. The tool provides details on whether the page is indexed, if there are crawl issues, or if specific errors prevent indexing. Use this information to identify if the page has technical problems, such as blocked resources or server errors, and address these issues to improve your page’s chances of being indexed.
What steps should I take if the URL Inspection Tool indicates a page is not indexed?
If the tool shows that your page isn’t indexed, verify that the page is accessible to search engines by checking your robots.txt file and noindex directives. Ensure the page complies with Google’s guidelines and is free of technical errors. You can request a recrawl through the inspection tool, and after fixing any issues, monitor the page to confirm it gets indexed.
How does the URL Inspection Tool assist in resolving duplicate content issues affecting indexing?
The tool helps identify if multiple URLs contain duplicated content, which can confuse search engines on which version to index. By inspecting specific URLs, you can see if Google considers them duplicates or canonical issues. Use this information to implement canonical tags correctly, consolidate duplicate pages, or set preferred URLs to improve indexing accuracy.
What should I do if the URL Inspection Tool reports crawl anomalies on a specific page?
<|p|>When encountering crawl anomalies, check the detailed error messages such as server errors or blocked resources. Fix server configuration issues, ensure that the page isn’t blocked by robots.txt, and verify that the URL loads correctly. Once resolved, request a recrawl to update the indexing status and prevent similar issues in the future.
Final Thoughts
Using the URL inspection tool for indexing issues is straightforward. Begin by entering the URL in the tool to analyze its current status. Review the insights provided, such as crawl errors or indexing problems. Address any issues identified to ensure proper indexing.
Focusing on how to use URL inspection tool for indexing issues helps maintain your website’s visibility. Regular checks allow you to identify and fix problems promptly. This proactive approach ensures your content reaches search engines effectively.